This content was reviewed by veterinarian Dr. JoAnna Pendergrass, DVM.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn a commission. Here’s how it works.
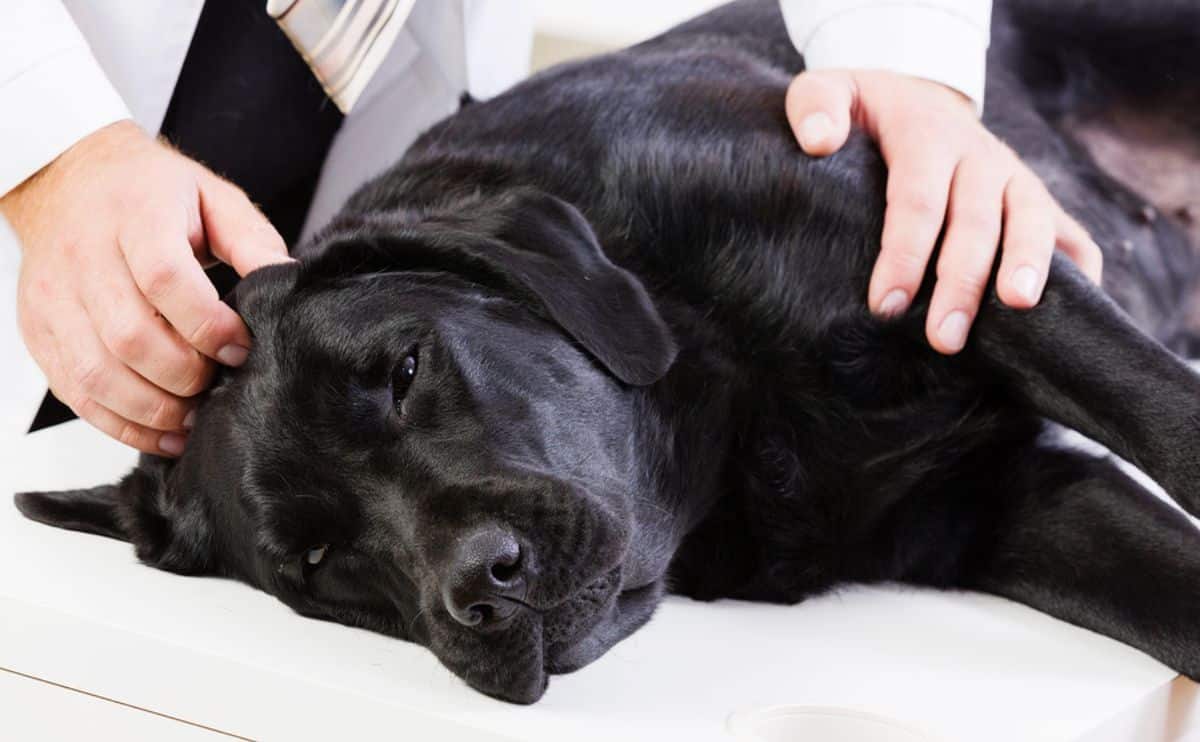

Seeing your dog in a life-threatening situation can be a frightening and stressful experience, especially if the dog is unresponsive. Equipping yourself with the knowledge to effectively recognize and take action in treating your dog’s condition can keep you calm and greatly increase your dog’s chance of survival. Two life-saving procedures you need to know are artificial respiration and cardiopulmonary respiration (CPR) for dogs. This article will outline how to identify whether your dog needs artificial respiration or CPR and how to perform those procedures.
Evaluate Their Condition

Before doing anything, you must evaluate your dog’s condition to know what to do. Time is of the essence in an emergency situation, so perform these evaluations as quickly as possible.
Is Your Dog Breathing?
- Hold the back of your hand or your cheek up to their nose and feel for air. Also, watch for the rise and fall of their chest.
- If your dog is breathing, immediately take him to your nearest veterinary clinic or emergency veterinary hospital.
- If they are not breathing, there is not enough time to rush to the vet. It is time to take immediate action.
- Start by checking their airway for any blockage.
- Pull the tongue forward as far as possible and gently try to remove any objects in the throat or mouth.
- If your dog reacts to you trying to remove the object, stop immediately to protect yourself from being bitten.
- If your dog doesn’t react, you will need to perform CPR.
Does Your Dog Have A Pulse?
- How to check a dogs pulse? The femoral artery, located on the inner thigh, is the easiest place to find your dog’s pulse. Run your hand along the inside of the hind leg until you are almost to the point where the leg joins with the body. There you should feel a slight dip where the femoral artery is closest to the skin. Use your fingers (not your thumb) to press down gently and feel for a pulse.
- If you cannot feel the pulse at the femoral artery, try just above the metacarpal pad (the large center pad) of your dog’s front paw or directly on top of the heart.
- Your dog’s heart is located on the left side of their chest. To find it, lay your dog on his right side and bend the front left leg so the elbow touches the chest. The point where the elbow touches the chest is the location of the heart.
If your dog has a pulse but is not breathing, you can perform artificial respiration (Skip down to Step 4 below). If your dog does not have a pulse, you will need to do CPR, which is a combination of artificial respiration and chest compressions.
How To Do CPR On A Dog: 6 Steps
Important: Do NOT practice CPR on a healthy dog. CPR can cause serious physical harm to dogs if performed unnecessarily. If your dog shows any signs of resistance to you performing CPR, then they may not need it.
CPR success rates are low even in a hospital with trained professionals. So, contact and begin transport to the nearest vet clinic ASAP. Don’t waste too much time attempting CPR yourself.
1. Position Your Dog For Treatment
- Lay your dog on a stable, flat surface with either their left or right side down. If you have a barrel-chested dog, such as a Bulldog, you can place your dog on their back.
- Straighten their head and neck as best you can to create a direct passage for their airway.
- Pull the tongue forward so that it rests against the back of their teeth and shut their mouth.
- Position yourself behind their back. You can either kneel or stand.
2. Find The Heart And Prep For Compressions

- Place both of your palms, one over the other with fingers interlaced, on top of the widest part of the rib cage, near the heart, but not directly over it. For smaller dogs weighing 30lbs (13.6kg) or less, cup your hands around the dog’s rib cage, placing your fingers on one side of the chest and your thumb on the other.
3. Begin Compressions

- Keeping both elbows straight and shoulders directly above your hands, push down on the rib cage in firm, quick compressions. Only compress 1/4 to 1/3 of the chest width.
- Repeat compressions at a quick rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. For smaller dogs, use your thumb and fingers to squeeze the chest to about a 1/4 or 1/3 of its width. Repeat this at a slightly quicker pace than for larger dogs, aiming for 17 compressions in 10 seconds.
Performing chest compressions gets tiring quickly. If you have someone helping you, switch off doing compressions with the other person every two minutes.
4. Begin Artificial Respiration

If performing CPR alone, give your dog artificial respiration after each set of 15 compressions.
- Begin by sealing the dog’s lips. Place your hand over the dog’s muzzle and ensure the mouth is completely closed.
- Next, place your mouth over the dog’s nostrils and blow gently, watching for the chest to lift and expand. If the chest does not rise, blow harder into the nostrils and check that the mouth is properly sealed.
*For smaller dogs, place your mouth over their entire muzzle. - Remove your mouth from the nose/muzzle between breaths to allow for air return.
- Administer one breath for every 15 compressions. (or two breaths every 30 compressions).
- If there are two people available to perform CPR, have one person do the compressions while the other gives artificial respiration after every five compressions.
If you are only performing artificial respiration, follow the same procedure as above for sealing your dog’s mouth, and administer one breath every two to three seconds at a steady pace of 20 to 30 breaths per minute.
5. Administer An Abdominal Squeeze

- Place your left hand under your dog’s abdomen and your right hand on top. Push down to squeeze the belly and assist in the circulation of blood back to the heart.
- Give one abdominal squeeze after each set of 30 compressions and two breaths.
6. Repeat
Check your dog every 1 to 2 minutes to see if they are responding. Continue CPR or artificial respiration until the dog starts to breathe on its own and has regained a steady pulse. If the dog is not breathing after 20 minutes, it’s time to consider discontinuing treatment, as it is not likely you will have success after this point.
Pet Ambulance Options
If someone else is with you during your dog’s emergency, you can have them search online for a pet ambulance. Some cities/states have pet ambulance options to increase their chances of survival during an emergency.
If an ambulance isn’t available in your town, have the person with you call your vet or emergency vet for feedback on the best course of action. Should you continue CPR in your current location or attempt to transfer the dog into the back of your car while you continue CPR? Or maybe the vet can come to you to help your dog.
Dog CPR Success Rate
“Statistics state that despite an initial 58% survival rate post initial CPR there is only a 3-6% survival rate to discharge in dogs and a 2-10% rate in cats. However, these figures differ significantly in patients which undergo cardiopulmonary arrest and CPR whilst under anaesthesia with a survival rate to discharge of nearly 50%.”
According to WebinarVet, April 2023
Precautions
CPR is a physically intense procedure that, when performed, can cause additional injury to your dog. These injuries can include broken ribs, pneumothorax (also known as a collapsed lung), and overall stress on your dog’s body. However, these injuries are treatable by a veterinarian, so it is not necessary to stop CPR for fear of harming your pet further. If you suspect that you may have broken a rib or otherwise injured your dog, simply continue with softer compressions.
Again, CPR and artificial respiration are NOT to be practiced on a healthy dog. However, it is recommended that you review some of the basics of the procedures so you will know how to perform them should your dog encounter a life-threatening situation. Go ahead and practice finding your dog’s pulse and the location of the heart, but do not perform compressions! In addition, have a list of local emergency veterinary clinics in an accessible site in your home or saved on your phone. Know their locations and which would be most convenient to get to in an emergency.
Dog CPR Demonstration (Video)
If you want hands-on training or more in-depth visual demonstrations, there are many options available. Watch a dog CPR video like this one, in which Elaine Acker, CEO of Pets America, demonstrates CPR for dogs in detail.
- Take a dog CPR class. Many pet-focused companies offer courses to learn pet first aid, including dog CPR. Pet Tech may offer an 8-hour program in your area, taught by a certified instructor that teaches a variety of first aid skills and offers a certificate once the program is completed. The Red Cross also offers courses, many of which are online and free.
- Talk to your veterinarian. At your next appointment, ask to go over the pulse points on your dog and discuss emergency best practices for your specific breed, size, and weight.
Additional Pet Safety Prep Tips
Preparation can be the difference between saving your dog’s life and running out of time. Save this guide and share it with other dog owners to ensure that every dog has the chance to enjoy another day. It is also crucial to be prepared for if and when an emergency strikes. Here’s a helpful disaster prep guide for pet owners, and be sure to have a dog first aid kit ready.
Tagged With: Emergency, Heart, Reviewed By Dr. Pendergrass, DVM

